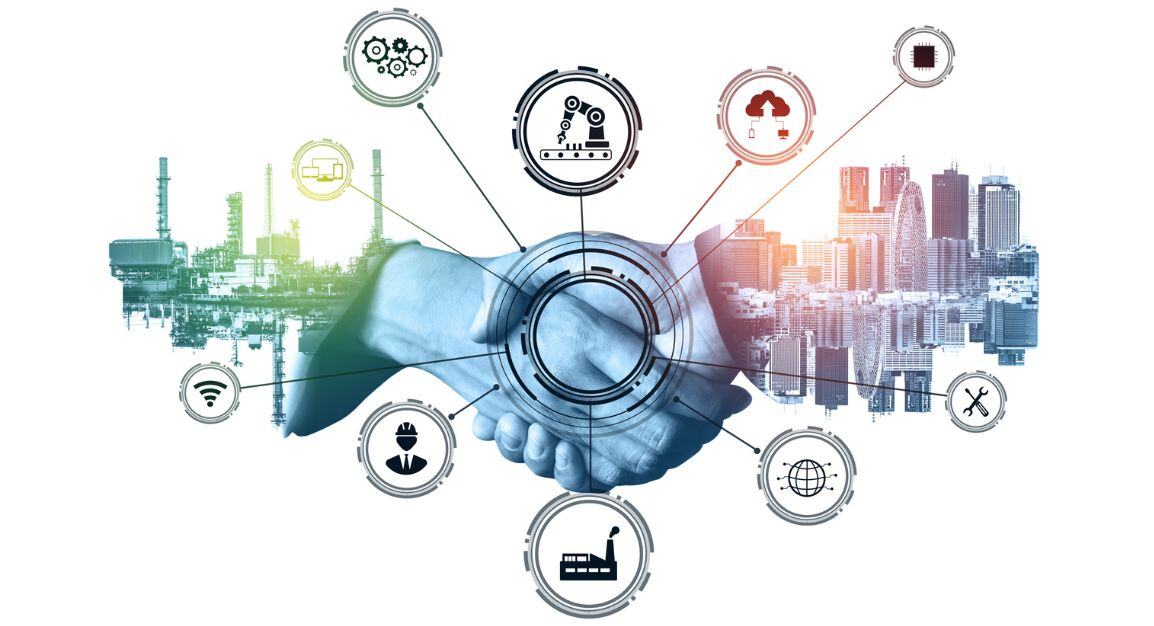
5 Things Food & Beverage Manufacturers Should Look for in their ERP.
Author: Lubin Hoque, Sales Director, Cooper Software
It’s London Tech Week next week. The event brings together innovators, investors and enterprise tech leaders to solve the world’s biggest problems. Topics such as artificial intelligence (AI) and sustainability are high on the agenda. And it might surprise you to learn, that this is incredibly relevant to manufacturing businesses. It is the innovation happening in these areas that will help them to navigate constant and demanding challenges, while dialling up business resilience.
Manufacturers faced intense challenges last year - from increased competition and complex customer demands, through to tightening regulations. To stay competitive into 2025 and beyond, adopting new technologies, prioritising efficiency and optimising operations will be central to mitigating instability. Let’s explore what the industry has to say...
1. AI, managing data, and dynamic planning
IDC predicts that within the next three years, investment and demand for AI and data pattern recognition is expected to rise by 40 percent. The suggestion here is that AI will become an indispensable tool for manufacturers, with Industry 4.0 and the emerging Industry 5.0 creating an unmanageable volume of data for effective human use.
The opportunity for manufacturing businesses is in the ability of AI to swiftly analyse real-time production data by using historical data to identify patterns and anomalies. This is valuable for manufacturing businesses for several reasons:
- Optimising efficiency: identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks in the production process for immediate adjustments to improve productivity
- Cost reduction: minimising waste, reducing downtime, and optimising resource utilisation, leading to cost savings
- Quality control: detecting deviations from expected quality standards, allowing prompt corrective actions
- Predictive maintenance: predicting equipment failures or maintenance needs before they occur, reducing downtime and preventing costly breakdowns
- Enhancing product innovation: from insights into consumer preferences and market trends, enabling innovation
Manufacturers can also enhance their adaptability, reduce lead time, and minimise the impact of supply chain disruption for efficient production by embedding AI into their enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. By leveraging AI, ERP and enterprise asset management (EAM), manufacturers can optimise their inventory and resources with real-time machine data. Indeed, according to McKinsey, using AI pattern recognition tools can lead to a four percent increase in revenue, up to 20 percent reduction in inventory, and a decrease in supply chain costs up to 10 percent.
- Demand forecasting: enables businesses to optimise inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and avoid overstocking
- Price optimisation: powers dynamic prices adjustments based on demand and market conditions
- Supply chain optimisation: identifies inefficiencies, such as delays, disruptions, or bottlenecks
2. Circularity, reducing waste and efficient resources
The world is shifting. The circular economy has been accelerated by The European Green Deal, and 42 percent of global manufacturers worry about the lack of key supplies and the increasing costs for raw materials.
In addition, Bain & Consulting found that 33 percent of executives expect their industry to be disrupted by circularity start-ups that put products or materials back into the supply chain. So, it’s safe to say that reusing materials can build business resilience by reducing dependence on virgin materials and increasing profitability from the same product. It also powers traceability, allowing manufacturers to monitor materials, parts, and products throughout their lifecycle.
An often-overlooked step in circularity and sustainable business planning is design. In fact, design decisions determine a product's lifespan, materials, reparability, and end-of-life outcome, influencing 80 percent of its environmental impact. So, embedding circularity strategies into manufacturing business models will assist with reducing waste while using valuable resources more efficiently.
- Resource efficiency: emphasises the reuse, recycling, and refurbishment of materials and products. This reduces reliance on finite resources, minimises waste generation, and conserves raw materials
- Cost savings: through reduced procurement costs and by extending the lifespan of products through repair and refurbishment that lowers production and disposal costs
- Regulatory compliance: staying compliant with evolving regulatory requirements and mandates
- Resilience and innovation: by diversifying supply chains, reducing dependency on volatile commodity markets, and promoting innovation in product design, manufacturing processes, and business models
- Enhanced reputation: retaining brand equity, attracting environmentally conscious consumers, and accessing new markets and investment opportunities
Manufacturers recognise that digital transformation is crucial for improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer experience. Challenging times require a fresh approach. And accelerating innovation, resilience, and circularity is a means to assuring economic prosperity in the long term.
Further information: IFS.ai delivers Artificial Intelligence across all IFS capabilities
Talk to us.
Start a chat, call on 01383 840 700 or complete the form, we will respond to all enquiries.